If you want to clone this Mercurial (Hg) repository, use the following command :
hg clone http://hg.cerbelle.net/hg/rsstats/
hg clone --insecure https://hg.cerbelle.net/hg/rsstats/
cat << EOF > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cerbelle.list deb [trusted=yes] https://packages.cerbelle.net/debian unstable/ deb-src [trusted=yes] https://packages.cerbelle.net/debian unstable/ EOF
apt-get update
apt-get install rsstats
apt-get purge rsstats
gdebi rsstats_0.0.1-1_amd64.deb
or
gdebi-gtk rsstats_0.0.1-1_amd64.deb
or
apt-get install libopts25 libssl3
dpkg -i rsstats_0.0.1-1_amd64.deb
dpkg -P rsstats
chmod +x rsstats-0.0.1-linux.AppImage
apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev pkg-config
tar xvzf rsstats-0.0.1.tar.gz
cd rsstats-0.0.1
The default installation folder is /usr/local. You can add the standard --prefix argument to change the default installation folder to another location, such as --prefix=/opt/rsstats, for example.
./configure --disable-doxygen
make clean all check
You can install with the provided system
make install installcheck
or you can build the DEB packages by yourself (you'll need to install debuild from the dev-scripts package or dpkgbuildpackage from the dpkg-dev package) and follow the previous steps to use them :
make debian-deb
If you installed rsstats in the system's root (/), You should keep the build dir because you can use make uninstall to cleanly uninstall each installed file. If you installed rsstats in its own folder, you'll be able to simply delete this folder and should not need the build dir anymore.
cd ..
rm -Rf rsstats-0.0.1
You can remove the build dependencies if they were not already installed when you requested them. Otherwise, another application is probably depending on them and you should probably not remove them. I suggest to keep them, but if you really want to remove them, please do only remove the dependencies which were not already installed before the first step.
apt-get purge libssl-dev
apt-get purge build-essential pkg-config
If you remove libssl-dev, you have to ensure that libssl3 remains installed (I hope that you already had it on your system).
apt-get install libssl3
This tool is a commandline tool and the usage is the same in all the supported operating systems. Please continue with the usage documentation.
This project is managed with GNU Autotools (the magic behind "./configure && make all install"). It needs a unix-like shell command line which is native with all linux distributions, with MacOS, but not with Microsoft Windows.
For windows developpers, install either MinGW with MSYS2 or Cygwin. I recommend the first one because Cygwin needs runtime dependencies which needs to be packaged with the builds. Whatever the choice, I will not document here how to install the installations processes, please read the related install docs.
I assume that MacOS developers already have HomeBrew installed.
The project uses the Mercurial:https://www.mercurial-scm.org Version Control System and publish the reporitory on the internet. The first step is to download and install Mercurial.
apt-get install -y mercurial
yum install mercurial
brew install mercurial
A whole Cygwin or MinGW development environment is needed, thus I recommend to install a commandline mercurial client. And, given that Windows users prefer mouse over keyboard, TortoiseHg can be also installed to integrate Mercurial features in Windows file explorer.
apt-get install -y build-essential
xcode-select --install
Autotools generates files such as configure which are distributed with the sources to compile them. This project does not store generated files in the repository. Thus, starting from the repository means to have autotools installed, to generate all the files needed to compile the project.
apt-get install -y autoconf autogen libtool pkg-config
brew install autoconf autogen libtool pkg-config
apt-get install -y libssl-dev
brew install openssl@3
For the developers, libopt was already installed with autogen and is available system-wide. For the maintainers, to avoid the need for autogen, a copy of libopts in automatically distributed in the source package.
The mandatory libssl-dev and libssl libraries should already be installed previously to allow configure to be executed.
Optionaly, the check library can be installed to allow unittesting.
apt-get install -y check
brew install check
From here, all the development specific dependencies are installed, but the project also have build dependencies (libraries).
./configure
make astyle
make cppcheck
xdg-open cppcheck/index.html
make cppcheck-clean
Included by default in make all target
make html
make pdf
make -C doc clean
make all check
make clean
make DESTDIR=`pwd`/_inst install installcheck
make DESTDIR=`pwd`/_inst uninstall
make dist distcheck
make distclean
make linux-appimage
make linux-clean
make debian-deb
make debian-clean
apt-get install rpm
mkdir -p rpmbuild/{BUILD,RPMS,SOURCES,SPECS,SRPMS}
make redhat-rpm
make redhat-clean
make windows-zip
make windows-exe
make windows-clean
make macos-zip
make macos-dmg
make macos-pkg
make macos-clean
The following folder contains all the build files from the Buildbot CICD at each commit in the project repository : sources, cppcheck analysis, coverage and performances tests, compiled binaries for different operating systems (Linux, Windows, MacOS), packaged in different format (ZIP, DMG, PKG, DEB, RPM, EXE installer, ...) : Downloads
The Debian based distribution packages are available in a Debian format repository : Debian archive
Source RPM for el6
Binary RPM for el6.x86_64
Standalone self-contained AppImage
Compiled binaries in a tar.gz file
DMG image containing a folder, not an Application Bundle
PKG to deploy in the system
Compiled binaries in a ZIP file
Windows installer
Compiled binaries in a ZIP file
Source dist in a tar.bz2 file
Source dist in a tar.gz file
Source dist in a tar.xz file
Source dist in a tar.zip file
Doxygen code doc in a PDF file
Doxygen code doc published online
LCOV Coverage report online
CppCheck code static analysis
Unzip the archive with ditto :
ditto -x rsstats-0.0.1-macos.zip
or with the user interface by opening it.
I recommend either to move the folder in /opt or at your home's root, using the command line in a terminal or drag'n dropping the folder and in the Finder :
sudo mv macosinst /opt/rsstats
Delete the folder.
Open/Mount the DMG Image in the Finder. Drag'n drop the inside folder in your home or in /opt.
Delete the folder.
Open the file in the Finder or use the following command line in a terminal. Despite it is possible, I recommend not to install the package in the system's root. I recommend to install it in /opt/rsstats . It makes the uninstall easier and less risky for your whole MacOS system !
installer -pkg rsstats-0.0.1-macos.pkg -target /opt/rsstats
Uninstalling a PKG is always tricky and can be challenging (if not dangerous for the MacOS System) depending on the installation location. Please read carefully, use a PKG uninstaller application or keep rsstats installed.
First, get the package name (unique identifier) :
pkgutil --pkgs | grep rsstats
It should be net.cerbelle.pkg.rsstats. Then, get the installation location, with the package unique id :
pkgutil --pkg-info net.cerbelle.pkg.rsstats
If you installed rsstats in a separate subfolder, such as /opt/rsstats, you can delete this folder /opt/rsstats and skip the next two steps (file and folder deletion).
Otherwise, you need to delete each installed file from the list returned by the following command, but you need to check that each file can be safely removed (it belongs and is used only to/by rsstats.
pkgutil --only-files --files net.cerbelle.pkg.rsstats
Then, you need to do the same with the folders. If you deployed the package in the root of the system (/), I do strongly recommand to not delete the folders.
pkgutil --only-dirs --files net.cerbelle.pkg.rsstats
Finally, you can ask the system to forget that the package was installed and remove the package's meta-data.
sudo pkgutil --forget net.cerbelle.pkg.rsstats
xcode-select --install
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
echo >> /Users/fcerbell/.bash_profile
echo 'eval "$(/usr/local/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> /Users/fcerbell/.bash_profile
eval "$(/usr/local/bin/brew shellenv)"
brew install openssl@3 pkg-config
tar xvzf rsstats-0.0.1.tar.gz
cd rsstats-0.0.1
The default installation folder is /usr/local. You can add the standard --prefix argument to change the default installation folder to another location, such as --prefix=/opt/rsstats, for example.
./configure --disable-doxygen --prefix=/opt/rsstats
make clean all check
You can install with the provided system
make install installcheck
or you can build the DMG/PKG/ZIP packages by yourself and follow the previous steps to use them :
make macos-zip macos-dmg macos-pkg
If you installed rsstats in the system's root (/), You should keep the build dir because you can use make uninstall to cleanly uninstall each installed file. If you installed rsstats in its own folder, you'll be able to simply delete this folder and should not need the build dir anymore.
cd ..
rm -Rf rsstats-0.0.1
You can remove the build dependencies if they were not already installed when you requested them. Otherwise, another application is probably depending on them and you should probably not remove them. I suggest to keep them, but if you really want to remove them, please do only remove the dependencies which were not already installed before the first step.
brew uninstall pkg-config
If you remove openssl@3, it will break rsstats and probably your system, plesae do not.
This tool is a commandline tool and the usage is the same in all the supported operating systems. Please continue with the usage documentation.
rsstats-0.0.1-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
chmod +x rsstats-0.0.1-linux.AppImage
apt-get install build-essential libssl-dev pkg-config
tar xvzf rsstats-0.0.1.tar.gz
cd rsstats-0.0.1
The default installation folder is /usr/local. You can add the standard --prefix argument to change the default installation folder to another location, such as --prefix=/opt, for example.
./configure --disable-doxygen
make clean all check
You can install with the provided system
make install installcheck
or you can build the DEB packages by yourself (you(ll need to install debuild from the dev-scripts package or dpkgbuildpackage from the dpkg-dev package) and follow the previous steps to use them :
make debian-deb
If you installed rsstats in the system's root (/), You should keep the build dir because you can use make uninstall to cleanly uninstall each installed file. If you installed rsstats in its own folder, you'll be able to simply delete this folder and should not need the build dir anymore.
cd ..
rm -Rf rsstats-0.0.1
You can remove the build dependencies if they were not already installed when you requested them. Otherwise, another application is probably depending on them and you should probably not remove them. I suggest to keep them, but if you really want to remove them, please do only remove the dependencies which were not already installed before the first step.
apt-get purge libssl-dev
apt-get purge build-essential pkg-config
If you remove libssl-dev, you have to ensure that libssl3 is installed (I hope that you already had it on your system).
apt-get install libssl3
This tool is a commandline tool and the usage is the same in all the supported operating systems. Please continue with the usage documentation.
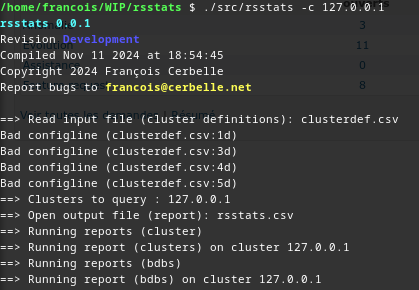
This tool generate the specified list of reports on the specified list of clusters in a CSV formatted output file.


Sample result output file : rsstats.csv
Help is available with the -h or --help option.
clusterdef.csv and can be specified with the -i option. It contains five mandatory fields per cluster (host, username, password, insecure, true by default, and cacert, file to load, empty by default) and one cluster per line, without header line. Given that it contains sensitive credential informations, it has to be protected. The CSV input format should conform to the RFC4180 :
a "sample" value => "a ""sample"" value")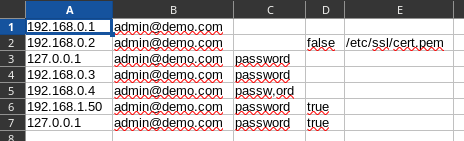
Example (Download link):
192.168.0.1,admin@demo.com, 192.168.0.2,admin@demo.com,"" 127.0.0.1,admin@demo.com,password 127.0.0.1,admin@demo.com,password,true 192.168.0.3,admin@demo.com,password 192.168.0.4,admin@demo.com,"passw,ord"
The default output CSV filename is rsstats.csv and can be specified with the -o option. It contains each report in an RFC4180 CSV compliant format concatenated in the same file. Thus, each report is RFC4180 compliant, but the whole output file is not.
You can list the reports to generate using the -r option with a comma separated list of report. It supports the special all and none names. The default value is all. You can use + and - to add or remove reports. For example, if you want all the reports but not the bdbs report, you can use : -r all-bdbs or --reports all-bdbs, if you want only the cluster report, you can specify -r none+cluster. The list of possible values is returned when asking the help with --help. There is also one special report, sample, which does not query any cluster, but writes sample data to the output file.
By default, the tool will iterate through the whole list of clusters defined in the configuration file (clusterdef.csv by default, which can be overriden using the -i option). You do not need to create a different file each time you want to execute the reports on a subset of your clusters. You can filter the enabled clusters using the -c option with a comma separated list of values from the first column of the configuration file, for example -c 192.168.0.3,192.168.0.4 or --clusters 192.168.0.3,192.168.0.4.
Open the archive with the Windows Explorer or any other archiver. Then, rename the wininst folder to rsstats-0.0.1 and copy it to a convenient location.
Run the RSStats installer from your Windows Explorer and follow the steps.
The installer automatically created an uninstall icon and registered the application in the Windows Registry. Thus, you can either run the RSStats Uninstaller or use Windows' Add/Remove programs
This tool is a commandline tool and the usage is the same in all the supported operating systems. Please continue with the usage documentation.